Aquarium Microbiome Analysis
Discover the complete bacterial ecosystem in your aquarium with Aquarium Microbiome Test. Get detailed insights into the health and balance of your marine ecosystem.


How It Works
Receive Kit
Your test kit arrives with everything you need
Collect Sample
Follow simple instructions to collect your sample
Ship Back
Use the prepaid label to send it back
We Analyze
Our lab analyzes your sample in detail
Get Results
Receive your comprehensive results report
Simple breakdown to categories
1. Microbial Diversity Gauge

2. Rank-Abundance Curve

3. Top Microbial Families

4. Pathogens

5. Bio-Filter Health

6. Cyanobacteria

7. Waste Degraders

8. Biofilm Formers

9. Pollutant Degraders

10. Sulphur Cycling

11. Algae Interactions

12. Phosphate Assimilation

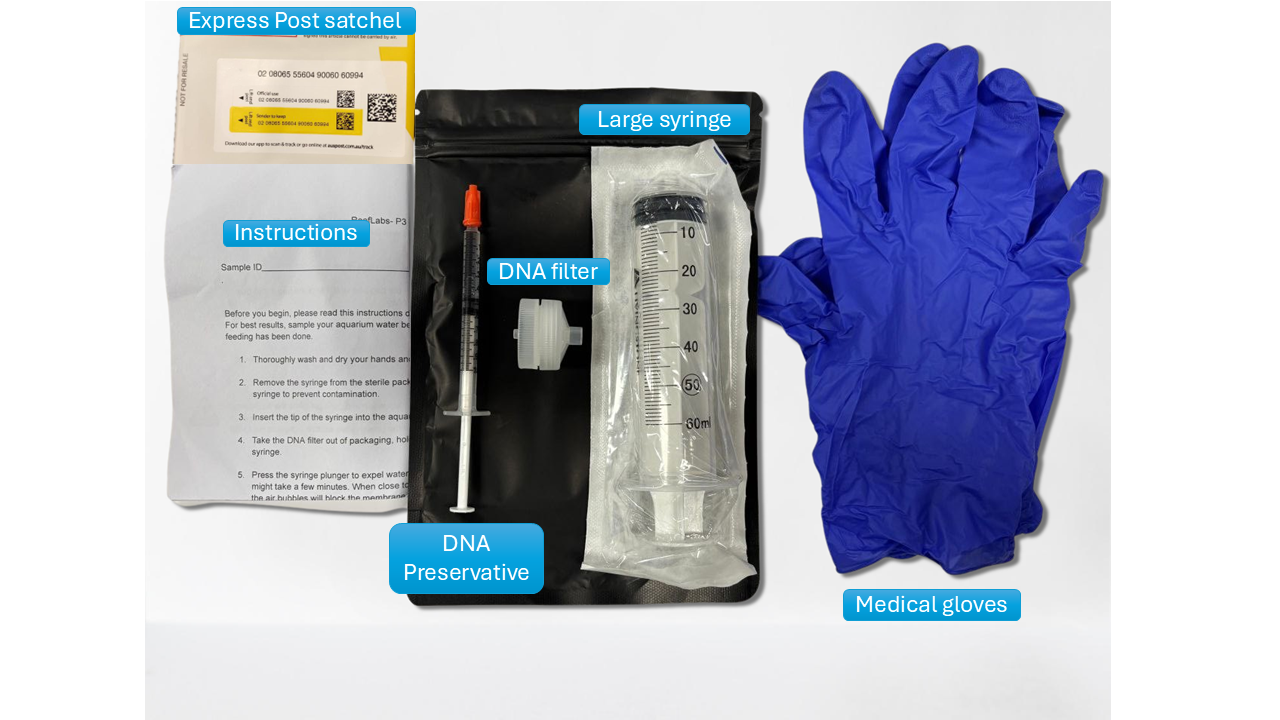
What You'll Receive
Complete Test Kit
Everything you need to collect and send your sample
Express Return Shipping
Pre-paid express shipping satchel included
Comprehensive Analysis
Advanced laboratory testing of your aquarium microbiome
Custom Recommendations
Personalized advice based on your specific results
~3-4 weeks Turnaround
Results delivered within 20-30 days from when your sample arrives at our laboratory.
Detailed PDF Report
Your aquarium microbiome results & insights delivered directly to your email



